Term for the biochemical metabolism of organic substances in the presence of oxygen. During respiration in animals or humans, for example, the cells burn the energy building block sugar to form carbon dioxide and water. However, aerobic conditions, i.e. sufficient oxygen, are required for complete combustion. In winemaking, oxygen causes oxidative processes; see oxidative maturation and reductive matur ation. Fermentation usually takes place for the most part under anaerobic conditions (absence of oxygen). Areobic conditions (presence of oxygen) are, however, important before or at the beginning of fermentation, as yeasts can only divide and multiply in an oxygen-rich environment. The scientist Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) reported as early as 1861 that yeasts consume much less sugar in an aerobic environment. In this context, one speaks of the Crabtree effect named after the English biochemist. The fermentation-like process of fermentation takes place under aerobic conditions.
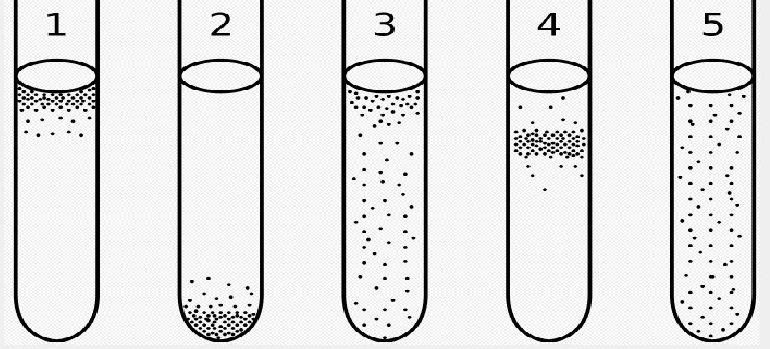
Graphic: Aerobic and anaerobic bacteria can be identified in liquid nutrient solution: (1) Obligate aerobic bacteria collect at the top where they get enough oxygen. (2) Obligate anaerobic bacteria collect at the lower end where there is no oxygen. (3) Facultative anaerobic bacteria are mainly found at the top because oxygen respiration is most effective; but they also grow in the deeper parts of the test tube. (4) Microaerophiles gather at the top, but not at the very top, because oxygen is optimal for them only in low concentrations. (5) Aerotolerant bacteria are not affected by oxygen and therefore distribute themselves evenly in the test tube.
Caption: WIKIPEDIA - Aeroby
Graphic: From User:Pixie derivative work: Marek M - Anaerobic, Public domain, Link
Voices of our members

In the past, you needed a wealth of encyclopaedias and specialist literature to keep up to date in your vinophile professional life. Today, Wine lexicon from wein.plus is one of my best helpers and can rightly be called the "bible of wine knowledge".
Prof. Dr. Walter Kutscher
Lehrgangsleiter Sommelierausbildung WIFI-Wien