The historical landscape at the lower course of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers in the south of present-day Iraq is considered one of the cradles of viticulture and wine culture. Around 4000 BC, the area was settled by the Sumerians and was subsequently divided into numerous city states. These were, for example, the cities of Haran, Cush, Ur (according to the A. T. of the Bible, the home of Abraham) and Uruk. The latter was ruled over by the legendary Sumerian king Gilgamesh, presumably in the period between 2750 and 2600 B.C. Under the famous king Hammurabi (1728-1686 B.C.), it reached its greatest expansion with the capital Babylon and encompassed almost all of Mesopotamia. In the 13th century BC, Babylonia fell to Assyria. The city of Babylon was completely destroyed in 689 BC by the Assyrian king Sanherib (705-681 BC), who made Nineveh the capital. The Babylonian king Nabupolossar (626-605 BC) overthrew the Assyrians' rule and probably had the Tower of Babel built. Under his rule, the Neo-Baylonian Empire was founded.
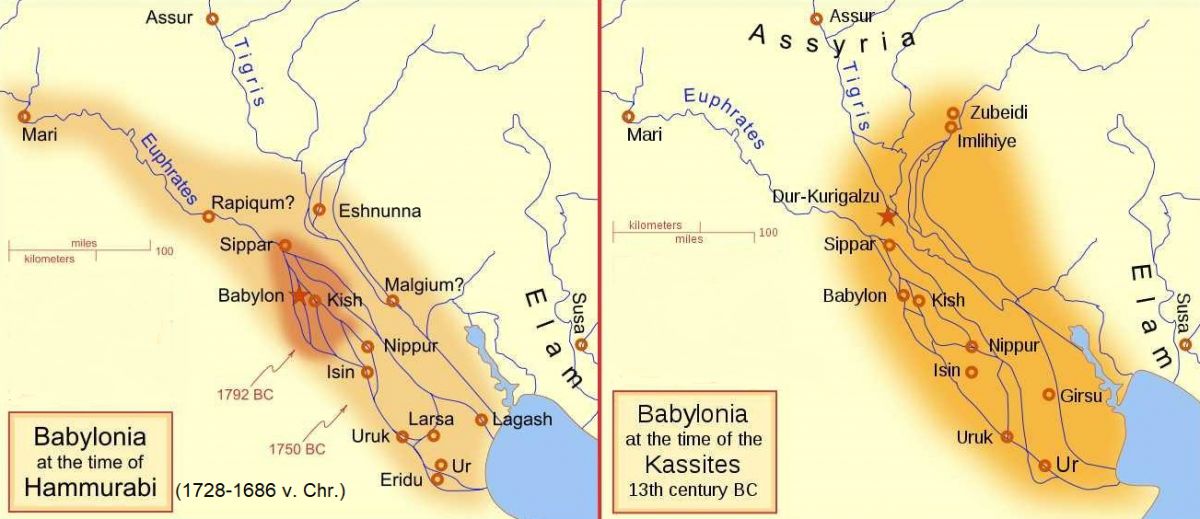
His son Nebuchadnezzar II (605-562 BC) created a great Babylonian empire, probably the famous Hanging Gardens of Semiramis - one of the ancient Seven Wonders of the World - were built under him. This king subjugated Egypt, Syria and Palestine, destroyed Jerusalem in 586 BC and deported a large part of the Israelites to the so-called Babylonian Captivity. An inscription about Nebuchadnezzar was found in a temple in what is now the ruined city of Babylon, mentioning wines from eight different regions, including a "drink of the mountains". The Greek historian Herodotus (482-425 BC) also visited Babylon on his travels; according to his own account, he still saw the Tower of Babel. He reports that wine was transported to Babylon on the Euphrates in palm wood barrels; the Greeks did not know wooden barrels for wine at that time (see also under Wine Vessels). In 539 BC, Babylonia was conquered by the Persian king Cyrus II (590-530 BC) and annexed to Persia. See also under Ancient wines.
Images: Bibelwissenschaft.de
Voices of our members

For my many years of work as an editor with a wine and culinary focus, I always like to inform myself about special questions at Wine lexicon. Spontaneous reading and following links often leads to exciting discoveries in the wide world of wine.
Dr. Christa Hanten
Fachjournalistin, Lektorin und Verkosterin, Wien