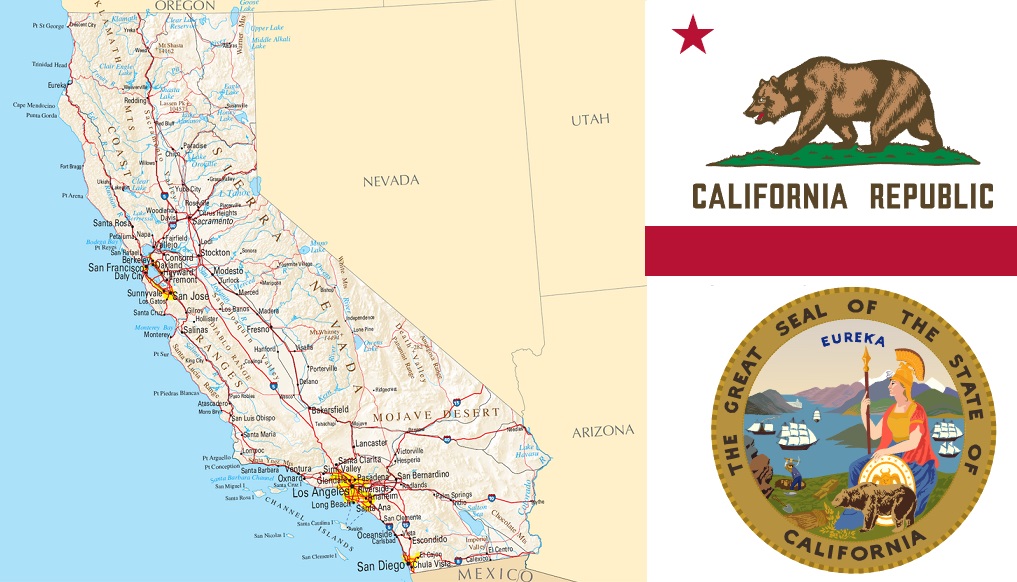
California
California, with its capital Sacramento, is the third-largest and by far the most populous state in the USA with an area of 423,970 km². It is located in the west of the country and borders the Pacific Ocean, the states of Oregon, Nevada and Arizona as well as the Mexican state of Baja California on the peninsula of the same name. California's official nickname is the Golden State. In 1846, US settlers declared California's independence (Bear Flag Republic) and proclaimed their own Republic of California, which led to the Mexican-American War. On 9 September 1850, California became the 31st state to join the USA.
History
California can be described as the motherland of viticulture in the USA. It also quite rightly bears the beautiful epithet "Wine State", as wine is an important economic factor here. The Spaniards introduced the Spanish Listán Prieto variety to Mexico in the 16th century, which was called Misión here and later Mission in California. In 1769, the Franciscan monk Junipero Serra (1713-1784) is said to have planted the first vineyard with this grape when he founded the "San Diego" mission in California (according to more recent sources, only ten years later). There were not the same difficulties here as on the east coast of the Atlantic, as the dry climate prevented fungal diseases and the vines thrived magnificently.
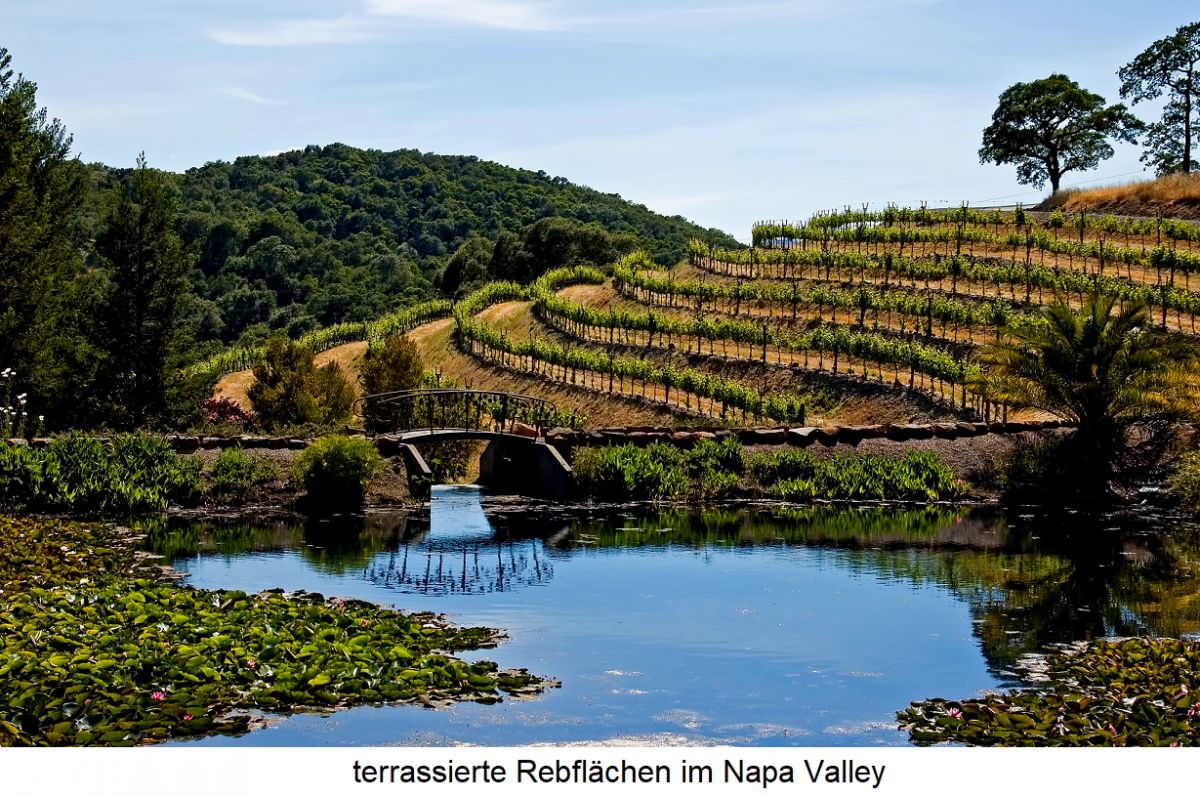

The wines were produced in a rather primitive way at the time; a contemporary report provides information about this: a cowhide (wineskin) filled with crushed grapes hung between two trees, in which the fermentation took place. At the bottom was a stopper which was simply pulled out to fill a cup of wine. The Mission wine was usually distilled into schnapps and used to spritz the remaining wine. Around 1833, a Frenchman with the symbolic name Jean-Louis Vignes (1780-1862) planted vines imported from Europe near Los Angeles for the first time. General Mariano Vallejo (1808-1890) was the last Mexican governor of California, which first became independent in 1846 and four years later in 1850 became the 31st US state. He had established a vineyard in Sonoma and was the first large-scale wine grower. In 1849, gold fever broke out in California and Zinfandel wine became the favourite drink of gold miners.
Viticultural pioneer Agoston Haraszthy
The big breakthrough came in 1860 with the Hungarian Agoston Haraszthy (1812-1869), who founded the Buena Vista Winery in Sonoma and introduced hundreds of European grape varieties. In the immediate neighbourhood, the German Jacob Gundlach founded a winery, which was reactivated in 1973 under the name Gundlach-Bundschu. Another pioneer was Prussian-born Charles Krug (1825-1892), who founded the Charles Krug Winery in St Helena in Napa Valley in 1861 and trained young winemakers. French-born Paul Masson (1859-1940) became famous from 1892 with his sparkling wine and was dubbed the "Champagne King of California". By the end of the 19th century, a diverse wine culture had developed with high-quality wines made from imported European vinifera varieties.
University of California
Around 1880, the University of California founded a wine research centre in Berkeley, which later became Davis. By 1890, one million hectolitres of wine had already been produced. The phylloxera catastrophe from 1880 destroyed many vineyards, but they were rebuilt. However, Prohibition (1920-1933) brought about the total decline of American wine culture. It was not until the 1950s that a revolution began. It began with small wineries experimenting with Chardonnay and Pinot Noir as well as French oak barrels. The pioneers responsible for the revival were Robert Mondavi (1913-2008), who founded his first winery in Oakville in Napa Valley in 1966, and Joe Heitz (1919-2000). Both were supported by the famous oenologist André Tchelistcheff (1901-1994). The high quality of Californian wines was also confirmed by an already legendary wine tasting (Paris Wine Tasting).
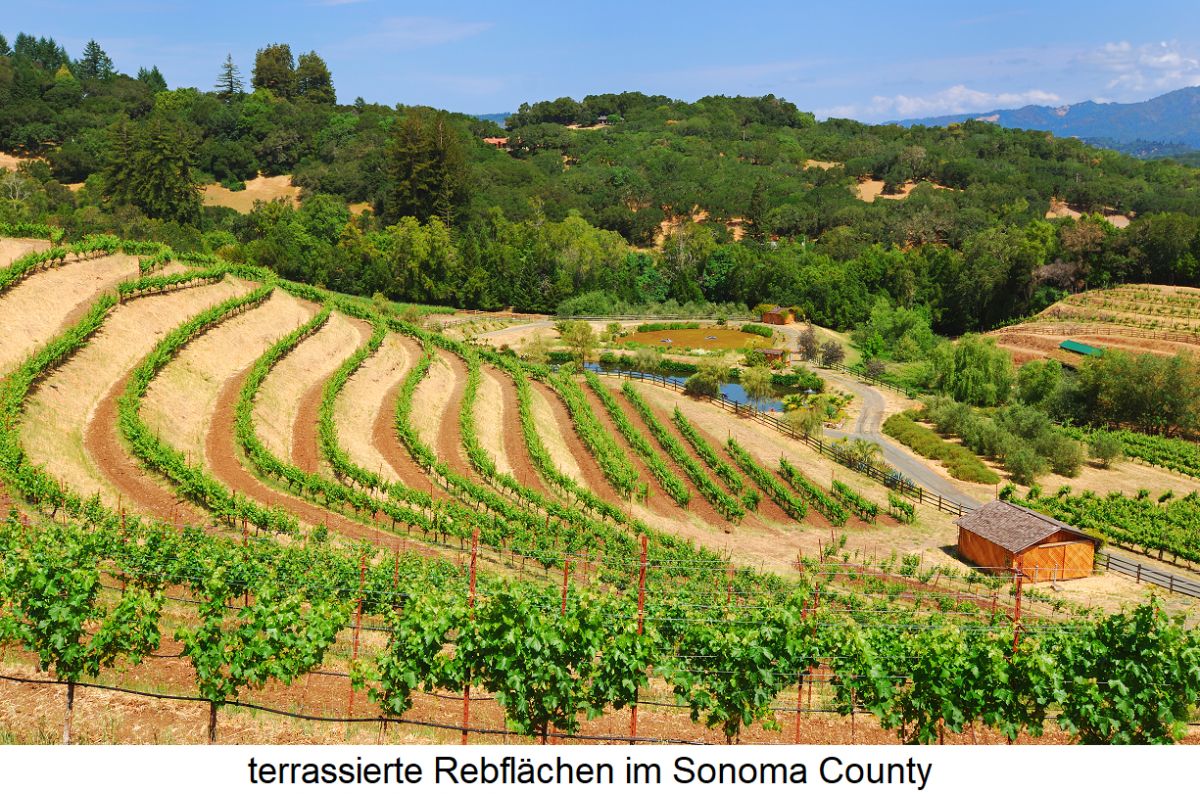

Wine-growing regions
California is divided into five major wine-growing regions, but these are by no means the same as the climatic regions listed below. The regions are divided into political counties (provinces), each with several AVA areas. However, these can also extend beyond the political county boundaries, as is the case with Wild Horse Valley (Napa and Solano counties) and Los Carneros (Napa and Sonoma counties):
Central Coast
The region covers around 25,000 hectares of vineyards. It forms a 560 km long strip from the north south of San Francisco Bay to Los Angeles in the south.
Central Valley (Delta & Inland)
This huge region comprises 140,000 hectares of vineyards...
Voices of our members

Serious sources on the internet are rare - and Wine lexicon from wein.plus is one such source. When researching for my articles, I regularly consult the wein.plus encyclopaedia. There I get reliable and detailed information.
Thomas Götz
Weinberater, Weinblogger und Journalist; Schwendi