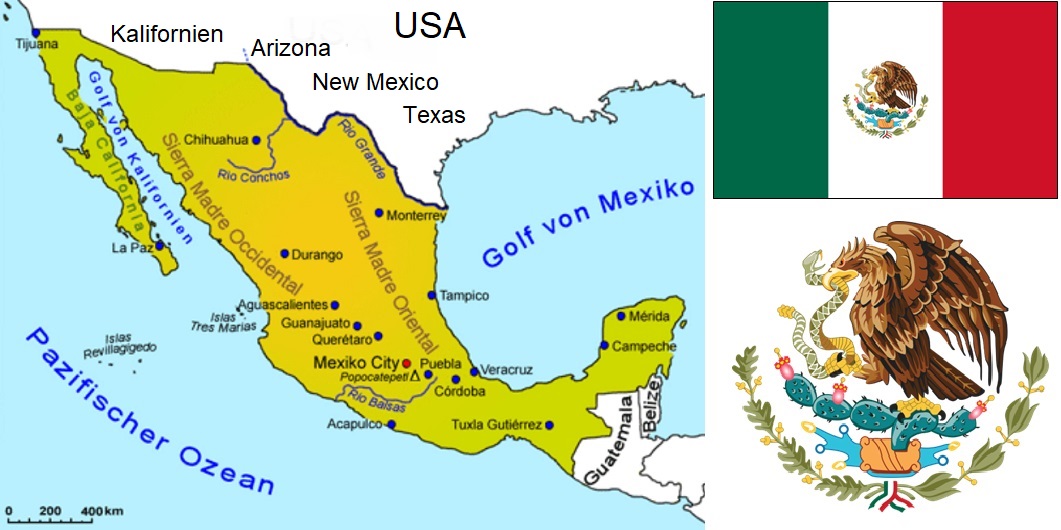
The presidential Republic of Mexico (Spanish: México, also known as Méjicoin in Spain) North America with its capital Mexico City covers 1,972,550 km². It borders the USA to the north (from west to east the states of California, Arizona, New Mexico and Texas), the Pacific Ocean to the south and west, Guatemala, Belize and the Caribbean Sea to the south-east, and the Gulf of Mexico to the east. In the north-west is the Baja California peninsula with a length of 1,200 kilometres. To the east, the Yucatán Peninsula, which Mexico shares with Guatemala and Belize, juts out into the Gulf of Mexico.
History
Mexico is the oldest wine-growing country on the American double continent or the New World. The Spanish conquistador Hernando Cortez (1485-1547) may have had vines planted as early as 1522. He issued the macabre authorisation to plant a thousand vines for every hundred dead Indians. According to another version, 100 Indians could be taken as slaves for every thousand vines. It is not certain whether the historical Misión (Listán Prieto) was involved. Franciscan monks are usually mentioned as having introduced this vine around 1540.
In 1568, gold was searched for in what is now the province of Coahuila. Although none was found, an oasis with water sources and countless wild vines was discovered within the desert. These discoveries motivated the Jesuits Jerónimo Ramírez, Francisco de Arista and Juan Agustín de Espinosa to found the mission of Santa María de las Parras in the Parras Valley in 1594 and make wine with the local grapes. Don Lorenzo García asked King Philip II (1527-1598) for the donation of land and permission to produce wine, which he graciously granted in 1597. This gave rise to the Bodega San Lorenzo, where the oldest winery in America is still run today under the name Casa Madero.
Subsequently, large quantities of wine and brandy were produced and exported to Spain. At the time, the vineyards covered around 70,000 hectares. Mexico had become too strong a competitor for Spain. For this reason, the Spanish crown under Charles II (1661-1700) issued a ban on wine production in 1699. Cultivated areas were even to be cleared. This was intended to boost Spain's wine export business. The colonists were only just able to negotiate a quota for religious purposes, i.e. for the production of mass wine, which served as a cover for daily needs for many decades.

Viticulture in the modern era
The Concannon family, viticultural pioneers from Livermore in California, introduced French varieties for the first time at the end of the 19th century. This was largely cancelled out by phylloxera and the Mexican Revolution led by the later President Francisco Ignacio Madero González (1873-1913) in 1910. At the end of the 1930s, Spanish civil war refugees, among others, reactivated viticulture. In 1948, the Asociación Mexicana de Vitivinicultores, which later became the Consejo Mexicano Vitivinícola, was founded as an industry association. Cotton farmers in particular switched to wine. The pioneers were Concha y Toro (Chile), Domecq, Freixenet and Torres (Spain). The consultant Dimitri Tchelistcheff (son of the legendary André Tchelistcheff) was instrumental in introducing new cellar techniques. After a crisis in the 1990s, more and more former grape producers are turning into small wineries. Overall, quality and consumption increased.
Wine-growing regions
The constant climate is characterised by very hot temperatures during the day and cold temperatures at night. The driest regions only have around 200 mm of rainfall per year, which is why artificial irrigation is the rule. At high altitudes, such as Parras, there are favourable conditions for growing wine. The particularly dry climate on the Baja California peninsula is cooled by the Pacific Ocean and the Gulf of California to the east with fresh breezes at night, even in the hot summer months.
Grapes are grown in a total of seven states. Baja California, by far the largest wine-growing region, is located in the north on the border with California and accounts for around 85% of production. The vineyards of the Aguascalientes wine-growing region are located on a plateau at an altitude of 1,600 to 2,100 metres above sea level. Scattered across the interior of the country are many other small wine-growing islands from Sonora in the north to San Juan del Rio north of Mexico City.
At the foot of the Sierra Madre Oriental, in the south-central region of the state of Coahuila, the fertile valley of Parras is an oasis in the middle of the desert. The town of Parras de la Fuente is the centre of Mexican viticulture with the huge Casa Madero winery mentioned above and Marqués de Aguayo (exclusively brandy). Other well-known Mexican wineries include Bodegas San Antonio, Bodegas Santo Tomás, Cavas de Valmar, L. A. Cetto and Monte Xanic.
Range of grape varieties
The vineyards cover around 50,000 hectares. Of these, only around 5,000 hectares are devoted to Celtic varieties with a wine production volume of 185,000 hectolitres. Around 500 labels are produced and bottled by over a hundred bodegas. However, the majority of the grapes are used for brandy(tequila), table grapes and sultanas. The "Presidente" brandy is one of the world's most successful spirits. Pulque (agave wine) is drunk in large quantities. It was not until the 1970s that noble varieties were introduced from Europe on a larger scale. The 2016 grape variety survey (Kym Anderson):
| Grape variety | Colour | Synonyms | Hectare |
| Sultana | white | Sultanina, Sultaniye | 841 |
| Cabernet Sauvignon | red | - | 756 |
| Mazuelo | red | Carignan, Cariñano | 448 |
| Merlot | red | - | 391 |
| Salvador Noire | red | Pate Noir, Salvador | 350 |
| Chenin Blanc | white | - | 275 |
| Muscat Blanc | white | - | 246 |
| Fiesta | white | - | 230 |
| Tempranillo | red | - | 229 |
| Nebbiolo | red | - | 180 |
| Cardinal | red | - | 168 |
| Syrah | red | Shiraz | 145 |
| Garnacha Tinta | red | Grenache Noir | 140 |
| Durif | red | Petite Sirah | 133 |
| Sauvignon Blanc | white | - | 120 |
| Palomino | white | Palomino Fino | 109 |
| Jacquez | red | - | 80 |
Map: © Goruma
Flag: by Alex Covarrubias, Public domain, Link
Coat of arms: by Alex Covarrubias, Public domain, Link
Baja California: by Gabriel Flores Romero, CC BY 2.0, Link
Source Viticulture in modern times: ProWein
Voices of our members

There is a vast number of sources on the web where one can acquire knowledge about wine. But none has the scope, timeliness and accuracy of the information in the encyclopaedia at wein.plus. I use it regularly and rely on it.
Sigi Hiss
freier Autor und Weinberater (Fine, Vinum u.a.), Bad Krozingen