Also referred to as residual sweetness (RS), the amount of sugar in the wine that is achieved by a natural end to fermentation or by deliberately stopping it. Various methods or agents are used to remove or kill the yeasts or at least inhibit their activity to a great extent. These include, for example, filtering the fermenting wine (removing the yeast cells), cooling to minus 3 to 2 °Celsius (stabilisation), adding sulphur, briefly heating to 75 °Celsius or, in the case of certain wines, spriting, i.e. adding pure alcohol (killing).
Designations for the sugar content
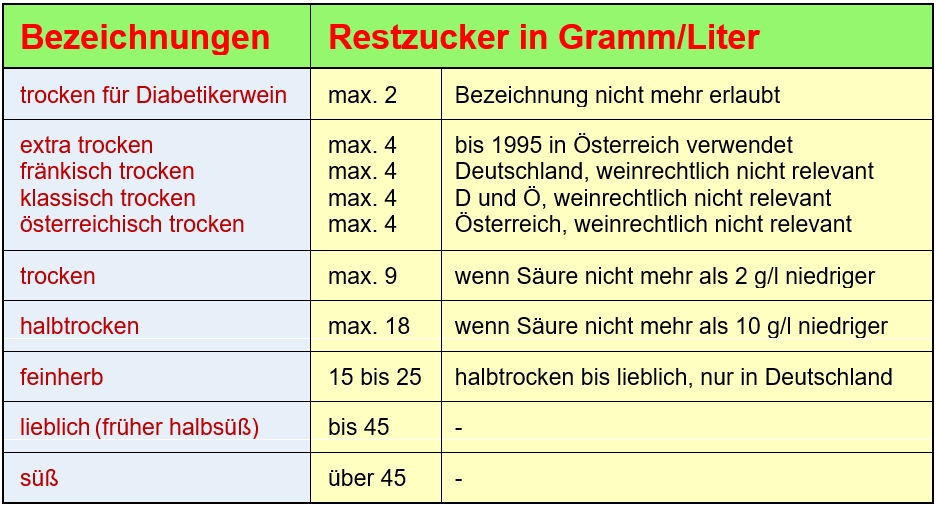
The residual sugar consists mainly of the sugar type fructose (fruit sugar), because glucose (grape sugar) is converted more quickly into alcohol and carbon dioxide, as well as a small proportion of non-fermentable sugars (pentoses). The remaining sugar content can be indicated on the label in the form dry, semi-dry, feinherb, medium sweet or sweet, as regulated by wine law. There are other country-specific designations, but these have no legal significance for wine. The previously common term diabetic wine is no longer permitted for consumer protection reasons.
Perception of sugar
The subjective perception of sweetness in wine, especially with high acidity, can differ relatively strongly from the actual analysed values. The lower the acidity, the sweeter and more concentrated the wine appears, as is the case with typical Sauternes wines. Wines with a low residual sugar content can be perceived as sweet if the acidity is low, while wines with a high residual sugar and acidity content appear dry.
Due to their carbon dioxide content, sparkling wines have different residual sugar levels and, in some cases, different terms than still wines. As a rule, a wine contains between 4 and 50 g/l of residual sugar, depending on the ageing process or wine type, and this can go up to 250 g/l for certain sweet wines (even up to 450 g/l for Tokaj Eszencia ). The residual sugar is not reduced during the ageing or bottle ageing of a wine. Under ideal fermentation conditions (warm fermentation), a wine can ferment down to a residual sugar content of 0.7 g/litre. Complete fermentation to 0 g/l is not possible under natural conditions, as there are always residues of non-fermentable sugars. This is why even a dry wine still contains a small amount of sugar. Wines with a content of less than 4 g/l are considered "fully fermented" (very dry). The content can also be increased by sweetening (adding sugar in various forms) in accordance with legal regulations.
Adding sugar to wine
Residual sugar can trigger unwanted bottle fermentation or form undesirable acetic acid and carbon dioxide. This is prevented by prior filtration (removal of yeasts) or pasteurisation. In a wine analysis, the residual sugar is determined in g/l as reducing sugar. The sweetening of wine, which is regulated by wine law, is known as the imparting of residual sweetness. In contrast, the addition of sugar to increase the alcohol content is called enrichment. The methods for determining the residual sugar content are listed under sugar content.
Further information
For the production of alcoholic beverages, see Champagne (sparkling wines), Distillation (distillates), Speciality wines, Spirits (types), Winemaking (wines and wine types) and Wine law (wine law issues).
Table: Norbert F. J. Tischelmayer
Voices of our members

In the past, you needed a wealth of encyclopaedias and specialist literature to keep up to date in your vinophile professional life. Today, Wine lexicon from wein.plus is one of my best helpers and can rightly be called the "bible of wine knowledge".
Prof. Dr. Walter Kutscher
Lehrgangsleiter Sommelierausbildung WIFI-Wien