Term (from Greek taxis = order, nomos = law) for categorisation in a hierarchical system. In biology (the science of living things), living things such as animals, plants and viruses are categorised and classified hierarchically into groups (taxa) according to their natural relationship. This categorisation into a hierarchical system is traditionally associated with the classification into a certain rank, such as species (spezies), genus (genus) or family (familia). The first attempts were made in ancient times, for example by the Greek naturalist Theophrastus (370-287 BC).

Carl von Linné
The Swedish botanist Carl von Linné (1707-1778) developed the foundations of modern taxonomy and introduced the concept of species into biological systematics. In his two-volume work "Species Plantarum", published in 1753, he described all the plants known to him on 1,200 pages with around 7,300 species. Among other things, the plant genus Vitis(grapevine) was described here for the first time. Together with the work "Systema Naturæ" published in 1758, this established the scientific nomenclature still used today in botany and zoology.
However, Linne's classification system did not yet include all the categories and levels used today. However, these are not always used for all plants or animals. The respective use simply depends on how complex the respective units are. The three main categories almost always mentioned in specialised sources are family-genus-species. Each category can be broken down into "subcategories" (subspecies). Similarly, a "superlevel" can be created as the last sublevel of a main category, which then stands above the next main category (superdiviso).
Species (kinds)
The term species is a fundamental category of biological taxonomy. However, the species is usually specified together with the first named genus - for example, in the case of humans as "Homo = human (genus) sapiens = rational (species)". However, a universally valid definition of the term has not yet been achieved. In biology, there are at least three species concepts that lead to overlapping but not identical classifications. In the concepts commonly used today, the term "species" usually refers to a group of living beings that have so many distinctive morphological (shape and form or their changes in the course of evolutionary history) or physiological characteristics in common that they are considered distinct from any other group of living beings.
Interbreeding
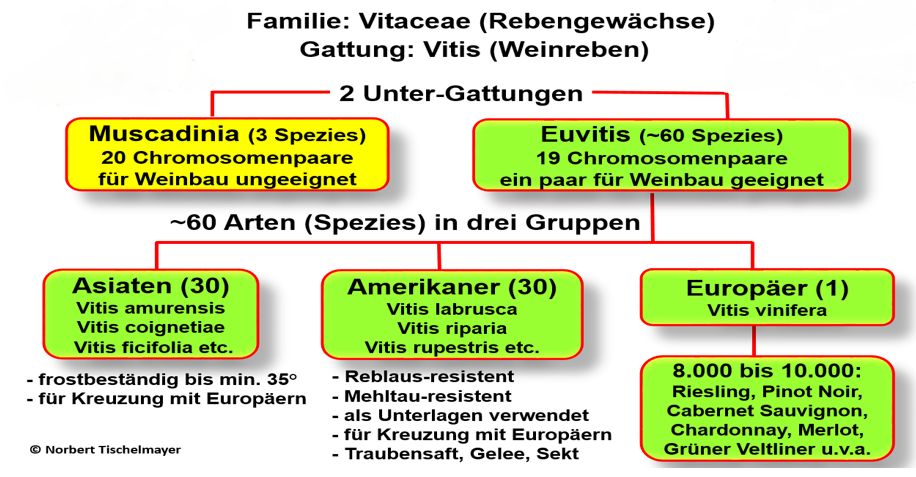
According to another view, those organisms and their direct descendants belong to a species that (can) reproduce with each other naturally by producing fertile offspring. A third view restricts the concept of species to organisms that share an ecological niche within an ecosystem. Reproduction or crossbreeding between two different species is not possible in principle for genetic reasons, although it is possible in most cases with grapevines, such as the two species Vitis vinifera and Vitis labrusca. These so-called interspecific crosses are generally referred to as hybrids, although strictly speaking crosses within a species (intraspecific) are also hybrids.
As a rule, crossbreeding between species of two different genera is very difficult or even impossible, although genus hybrids do occur in nature. This means that when assigning animals or plants to the respective levels, consideration was not always given to the possibility of reproduction.
Taxonomic systems
In practice, there are several systems that differ in detail, especially in zoology and botany. The taxonomic system most commonly used for plants, including grapevines, is described under Vine systematics.
Further information
See also the keywords DNA, chromosome, American vines, Asian vines, European vines and grapevine family tree as well as lists of relevant keywords under vineyard area and grapevine.
Carl von Linne: by Alexander Roslin - Public domain, Link
Plant classification: by Georg Dionysius Ehret, Public domain, Link
Systema Naturae: by Carl von Linné, Public domain, Link
Graphic: Norbert F. J. Tischelmayer
Voices of our members

The wein.plus encyclopaedia is a comprehensive, well-researched reference work. Available anytime and anywhere, it has become an indispensable part of teaching, used by students and myself alike. Highly recommended!
Dominik Trick
Technischer Lehrer, staatl. geprüfter Sommelier, Hotelfachschule Heidelberg